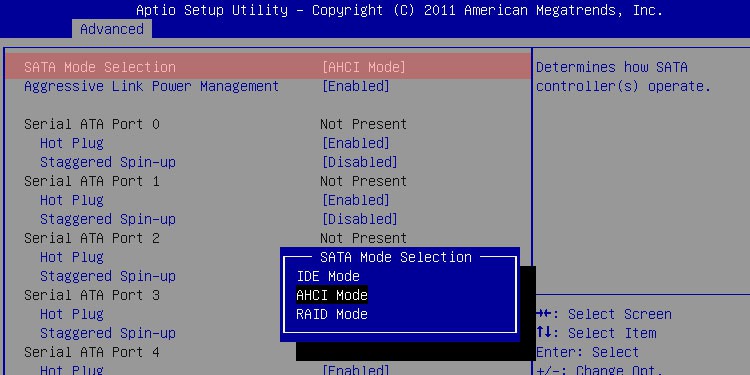
However, not every standard setting is the best option for all users – and some of the changes that might benefit you require a more in-depth knowledge of computers. Choosing between AHCI, RAID, and IDE for your SATA configuration is one of those things that can improve your entire computer experience but is a bit complicated.
What is SATA Configuration?
Your SATA configuration has to do with the way your computer stores and processes data. SATA stands for Serial Attached Technology Attachment because it describes a particular connection between multiple devices. When people talk about your SATA configuration, they’re talking about storage devices attached to the motherboard and where data is stored for long-term purposes. Newer drive types like Solid State Drivers and NVme drives don’t always use a SATA protocol. However, some SSDs are designed to attach to the motherboard with SATA cables because the connection type was so common on almost every PC for years. In general, devices that connect directly to the motherboard are faster than those using cables, especially if you have a PCIe 4.0 slot. IDE, AHCI, and RAID are different ways to manage your SATA devices. Which one works best depends on your computer, what drives you’re using, and how you intend to use them.
IDE, AHCI, RAID: What’s the Difference?
Understanding what IDE, AHCI, and RAID provide is a great place to start choosing a setup for your system.
IDE
IDE stands for Integrated Drive Electronics and is the oldest SATA protocol. Modern systems rarely use it because it’s slower and offers fewer options than AHCI. It is generally provided as a way to connect legacy hardware that won’t work with other configurations. Ultimately, the only reason to use IDE is if you don’t have any other options because you’re using an older system that doesn’t offer them. IDE is supported by almost every operating system and is widely available.
AHCI
AHCI stands for Advanced Host Controller Interface, and it’s the alternative to IDE. It’s newer protocol still stores all the information on the assigned drive. Its job is facilitating data transfer from the RAM to the hard drives. AHCI offers the following benefits over IDE:
Native command queueing, NCQ is a way of prioritizing how tasks are handled when data is moved around. Older systems would handle tasks in the requested order, even if that wasn’t the most efficient way to complete every job as required. Hot plugging is a feature that lets you plug in new disk drives even when the computer is switched on. This is useful, especially when you’re troubleshooting or if you frequently have to attach and reattach drives to your computer.Speed is one of the most significant benefits of AHCI over IDE. In most cases, it’s much faster. IDE is the best choice if you’re using older hardware that won’t support it.
While people can get by with IDE, it’s better to use AHCI unless your equipment is very old. Sometimes using SSDs in AHCI can also introduce more latency to your system.
RAID
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a very different option from the others because it uses a virtual storage system to manage your disk drives and saved files. Multiple disks are used in a virtual array to keep your information stored across more than one disk, which has some profound benefits. RAID isn’t actually a SATA technology, but you still choose it from the same options because it handles how your data is stored and managed. RAID generally requires you to enable AHCI. You may have to check your BIOS options to ensure it’s turned on before creating a RAID array. One of these is that specific RAID arrays can help you with your data backup. Most RAID arrays are fault-tolerant because they back up the data on other drives. It also offers more security than standard SATA options. However, the safety and speed you get from a RAID setup depend on your configuration. The types of disks you have can also determine whether you want to try a RAID configuration. Some are better for HDDs, while others work better with SSDs.
Different RAID Configurations
RAID actually has a lot of other options depending on how many drives you have. RAID 2, 3, and 4 are rarely used anymore and probably not the best choices for your RAID array.
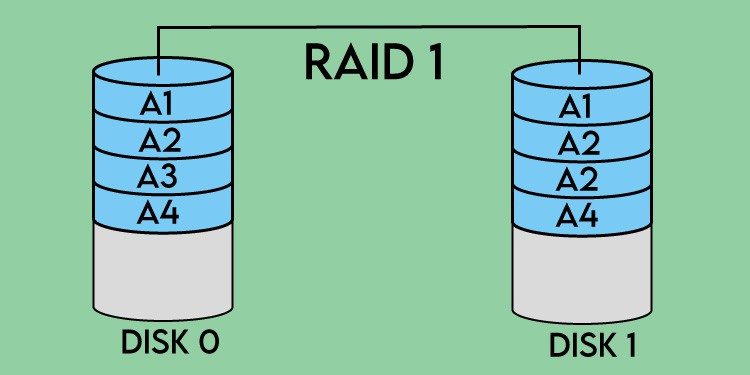
RAID 0 is a fast configuration that shares data across multiple disks but doesn’t create backups. It’s speedy because it writes and reads from more than one disk simultaneously. It’s meant for when you need the most possible speed and don’t mind the risk of losing your data. If one drive dies, all your data is lost. RAID 1 copies the data between more than one disk so that you don’t lose everything if one drive dies. It’s also faster than RAID 0 with read speeds, though write speeds will suffer a bit in this configuration. It is incredibly reliable because data is mirrored on each disk in the array. RAID 5 and 6 require three and four drives minimum, respectively. They work similarly to RAID 0 and RAID one because your data is stored on multiple disks and backed up on the others. You can lose one disk in RAID 5 or two disks in RAID 6 without suffering complete data loss. However, rebuilding the system after a disk fails takes a lot of time, and the performance of the entire array suffers until it’s restored.RAID 10 requires at least four disks. It’s fast and backs up your information better than any other array.
Remember that RAID arrays can reduce your total drive space since certain setups save and store data in multiple places. You have to decide your goals and resources to determine which array suits you. If you have many disks, RAID 10 might provide the most helpful setup. However, it depends on whether you want to prioritize speed, backups, and whether the read or write rate is most important.
Which Option is Right for My Computer?
There are a few things to think about when you’re trying to decide what SATA configuration to use.
If you’re using older hardware, check to see what SATA controller it supports. Some older ones might not even work with AHCI or RAID. Knowing in advance can help you avoid problems later. RAID is often used in server environments to back up the data and improve certain read or write speeds, depending on what the servers are used for.If you don’t mind doing more PC management, RAID might be a good choice. If you prefer to set things down and leave them alone while you use your computer, consider using AHCI. RAID arrays can’t be updated as quickly as adding a new drive, so if you ever need more disk space, you’ll have to set up a new RAID array. RAID sometimes works better for multiple arrays of HDDs for servers and file sharing systems unless all of your SSDs connect with SATA cables. The speed of SATA drives plugged directly into the motherboard is so much higher than SATA-connected drives that the RAID array just isn’t as necessary or helpful with an SSD NVME setup.
It comes down to what kind of system you’re running. For home users, ACHI is generally acceptable. If you’re looking to create a more advanced setup and have a lot of disks to work with, consider RAID.
Is RAID or AHCI Better for Gaming?
Most people will do better with AHCI for gaming. RAID is great at many different functions but isn’t the best choice for gaming, even if you’re setting up a RAID 10 array. It takes more disks, reduces your overall memory, has a higher failure rate, and won’t improve your speeds very much. One of the better options is to switch your gaming to an SSD or an NVME drive. Both of these options will be significantly faster than an HDD. If you want to game with a RAID array, consider choosing RAID 0 and storing anything you care about elsewhere so that if the drive fails, you only lose game files that are easy to download and restore.
Are There Any Other Protocols to Consider?
The most recent protocol you can use instead of AHCI is called Intel Optane memory. You have to have a specific device designed to work with that option to use it. If you aren’t sure whether you have an Intel Optane product, check or switch to another option.
When Should I Change My Configuration?
You need to select which protocol you want to use before you install your operating system since you make the selection in BIOS. Many Windows users have found that the operating system won’t load the AHCI driver unless the option is selected before the operating system was installed. The reason for this is the AHCI drivers won’t be recognized by an operating system that wasn’t implemented with them in place. People often run into this problem when they try to upgrade their hardware without reinstalling their operating system and decide to change the SATA configuration.
Is AHCI Slower than RAID?
In general, AHCI is probably slower than most RAID arrays. Anything that uses HDDs instead of SSDs or NVME drives will be slower because of the data transfer limits.
Does AHCI Improve Performance?
When it comes to IDE versus AHCI, AHCI will usually improve performance. However, sometimes it’s subject to a bottleneck effect, depending on how it prioritizes pending tasks. Using RAID can undoubtedly be faster than AHCI, depending on the hardware and configuration.
Can I Use AHCI With an SSD?
You can use AHCI with any disks that support the protocol, including SSDs. Just check the documentation on your drive to see what SATA protocols it supports. For example, I have two HDDs, an M.2, and an SSD in the computer I’m using. I also have AHCI enabled.